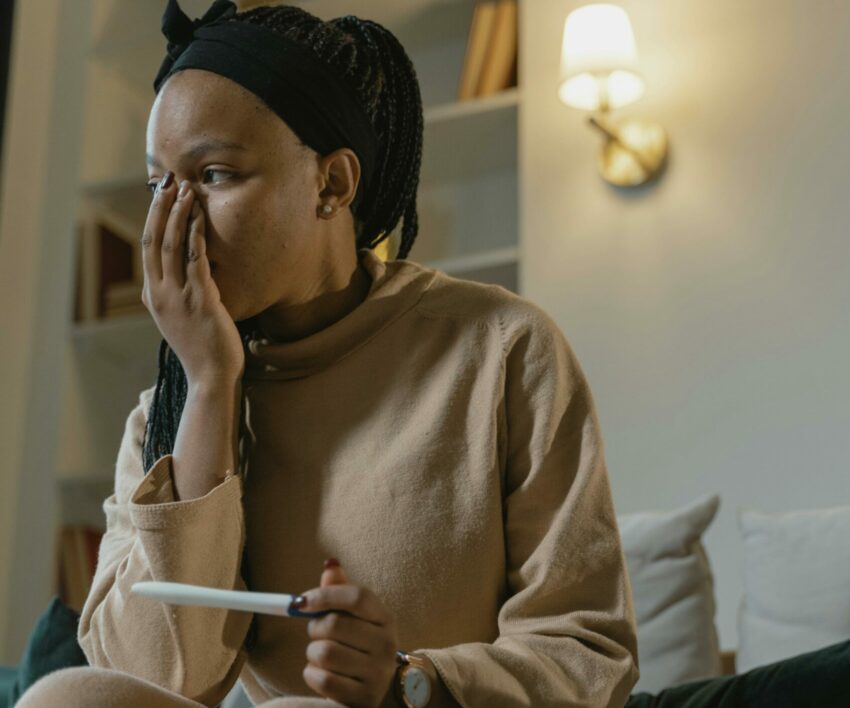
A woman’s reproductive health is of utmost importance and it’s always good for a girly to be in the know about what happens regarding that aspect of her life. Several common conditions affect a woman’s fertility and polycystic ovary syndrome is one of them.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal imbalance caused by high levels of androgens in the ovaries, leading to irregular menstrual cycles, missed periods, and unpredictable ovulation. It is said to be a common cause of infertility in women and those assigned female at birth, and can increase the risk of other health conditions.
“Small follicle cysts (fluid-filled sacs with immature eggs) may be visible on your ovaries on ultrasound due to lack of ovulation (anovulation). However, despite the name “polycystic,” you don’t need to have cysts on your ovaries to have.”
The National Health Services states that “Polycystic ovaries contain a large number of harmless follicles that are up to 8mm (approximately 0.3in) in size. The follicles are underdeveloped sacs in which eggs develop. In PCOS, these sacs are often unable to release an egg, which means ovulation does not take place.”
The above clinic lists more of the symptoms that indicate this condition, including:
- Abnormal hair growth
- Acne
- Obesity
- Darkening of the skin
- Cysts
- Skin tags
- Thinning hair:
- Infertility
According to the Mayo Clinic, this condition can be caused by insulin resistance, a hormone produced by the pancreas, which can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and increased production of the male hormone androgen, affecting ovulation.
It is believed to also be caused by genes, and inflammation, states Healthline. “Obesity is a major cause of insulin resistance. Both obesity and insulin resistance can increase your risk for type 2 diabetes. Women with PCOS often have increased levels of inflammation in their bodies. Being overweight can also contribute to inflammation. Studies have linked excess inflammation to higher androgen levels.”